Monday, July 23, 2018
WORKING OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
6:00 AM
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
The operational amplifier is a direct coupled , high gain, high input impedence , and low output impedence ,high bandwidth amplifier. The gain can be controlled by feedback by feedback . In short operational operational amplifiers are termed as "op-amp" ,op-amp are in performing various mathematical operation such as addition ,subtraction etc ,And it is mainly used in converting sine wave to square wave in future posts .
The block diagram of operational amplifier is shown below
if you want to understand the working of op-amp you need to understand working of differential amplifier . In my first post i briefly explained the working of differential amplifier . I think u read that
op-amp consists of 4 blocks
input stage :- Input consists of differential amplifier which gives high CMRR {The necessity of high CMRR is since it take 2 inputs, CMRR tells the ability to reject common signals [noise] & amplify differential signals} high input impedence , high voltage gain .
The operational amplifier is a direct coupled , high gain, high input impedence , and low output impedence ,high bandwidth amplifier. The gain can be controlled by feedback by feedback . In short operational operational amplifiers are termed as "op-amp" ,op-amp are in performing various mathematical operation such as addition ,subtraction etc ,And it is mainly used in converting sine wave to square wave in future posts .
The block diagram of operational amplifier is shown below
 |
| block diagram of operational amplifier |
op-amp consists of 4 blocks
input stage :- Input consists of differential amplifier which gives high CMRR {The necessity of high CMRR is since it take 2 inputs, CMRR tells the ability to reject common signals [noise] & amplify differential signals} high input impedence , high voltage gain .
Gain stage :- The gain of op-amp is further increased by gain stage, which consists of darlington pairs (CC-CC) AND (CC-CE) cascaded amplifier . here gain is the ratio of input by output and impedence resistance of ac circuit DC-LEVEL:-since op-amp is basically DC amplifier and no capacitor used , quiescent voltage shifts after every stage .To bring it back to the original level emitter follower is used as DC level shifter
Output stage :- output stage have low output impedence and should be able to supply high output current [ just remember the ohm's law as when resistance is low ,current will be higher ].it uses the pushpull amplifier to do like that .
when the inputs of an op-amp are grounded the output must be zero . but there is a small error voltage at the output due to the difference in Vbe values of input transistors.
thanks for reading the article , in next article we study by using the different feedbacks what will be the output and characteristics
 |
| circuit diagram og op-amp |
A positive input at the inverting terminal produces inverted (negative) voltage at output. A positive input at non inverting terminal produces [positive] or non inverting voltage at output .
CHARACTERISTICS OF OP-AMP
- OPEN LOOP GAIN :- The gain of the amplifier without feed back is called the open loop gain.Here feedback means process of taking a part of output and feeding it back to the input is called feedback . The main thing here feedback is done through resistor . there are two types of feedback are there ,they are 1)positive feedback and 2) negative feedback
- INPUT IMPEDENCE :- impedence as seen from the input terminals
- OUTPUT IMPEDENCE:- impedence as seen from the output terminals (It tells us how many number of devices at the output without getting loaded).
- BAND WIDTH :- Ideal op-amp the bandwidth is infinite , which means that op-amp provides amplified output for signals of frequency from 0 to infinity hertz without any attenuation.
- CMRR :- Indicates the ability of op-amp to rejects the common mode signals (noise ) and amplify differential signals .
- SLEW RATE :- The maximum rate of change of output voltage per unit time . This character indicates the ability to respond to variation in the input frequency .
- INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE :-
This is the small voltage that must be applied between the two input terminals to make output voltage zero . This is called balancing technique .
circuit diagram of input offset voltage - OUTPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE :-
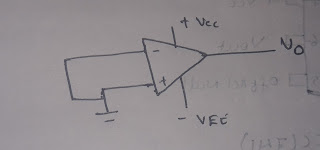 |
| circuit diagram of output offset voltage |
IDEAL AND PRACTICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF OP-AMP
CHARACTERISTICS IDEAL PRACTICAL
OPEN LOOP GAIN INFINITE 10^5
INPUT IMPEDENCE INFINITE M OHMS
OUTPUT IMPENDENCE ZERO OHMS
BANDWIDTH INFINITE FEW M HERTZ
CMRR INFINITE 90db
SLEW RATE INFINITE 0.5 V/Micro seconds
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE ZERO few milli volts
PIN DIAGRAM OF VARIOUS PACKAGES OF OP-AMP
 |
| pin diagram of IC [741] |
thanks for reading the article , in next article we study by using the different feedbacks what will be the output and characteristics
WORKING OF DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS
5:56 AM
DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER
Differential amplifier is a building block of IC amplifiers. It is direct coupled amplifier . { this means one end of the amplifier is connected to another by wire , unlike connected by resistors or transformers}. As the name tells us that " it amplifies the difference between the input signals . Operational amplifiers are made by using differential amplifiers ,so differential amplifiers are called as Building block of operational amplifiers.
The basic differential amplifier consists of two identical transistors Q1 ,Q2 , collector resistors RC1 & RC2 , emitter resistor RE . inputs Vi1 and Vi2 are given to the base of each transistors and outputs Vo1 ,Vo2 are taken out from collectors . Two power supplies vcc &vee are provided for the amplifiers .
MODES OF DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIES
- Double ended input & double ended output.
- Single ended input & single ended output.
- double ended input & single ended output .
- single ended input & double ended output.
WORKING OF DUAL INPUT BALANCED OUTPUT (1) DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIERS
working of differential amplifiers is analyzed by superposition theorem { considering one input is present and other input is grounded }
- considering Vi1 , grounding Vi2 :
here Q1 transistor acts as CE amplifiers , because input Vi1 is applied at base , amplified output Vo1 is taken at collector , hence Vo1 is out of phase with input Vi1 .
here Q2 transistor acts as CB amplifier because input is applied at emitter ,at collector a amplified output Vo2 is appears same as input
2. considering Vi2 , grounding Vi1 :
here Vi2 is the input applied at base hence transistor Q2 acts as CE amplifier , the amplified output Vo2 is out of phase with input Vi2 taken at collector.
Vi2 is the input to Q1 transistor applied at emitter hence Q1 acts as CB amplifiers , vo2 is the output obtained collector which is in phase with applied input .
When both the inputs is applied ,a output is measured between collectors
A= Vo/(Vi1-Vi2).
COMMON MODE OPERATION :
When the same input is applied to both the inputs of a differential amplifiers , the resulting operation is called common mode operation . usually DE refuses to amplify common mode signals .
If we consider dual input single output DE , then
voltage gain A = Rc/-2Re
DIFFERENTIAL MODE OPERATION :
When the two opposite polarity signals are applied to the two input of a differential amplifier , the resulting operation is called differential mode operation .
voltage gain is A=Rc/2re'
COMMON MODE REJECTION RATIO
The ratio of differential mode gain to common mode gain is called is called as CMRR .
The main objective of the differential amplifier is to amplify differential signals and rejects common signals such as noise . CMRR represents the ability of the differential amplifiers . Ideally CMRR is infinity .It is expressed in db.
thanks for reading the article . If you have any question plz comment .
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

